- Healthcare stakeholders are individuals or groups that influence, deliver, regulate, or are affected by patient care and health outcomes, including patients, providers, policymakers, and payors.
- Stakeholder engagement matters because healthcare priorities often conflict across clinical quality, cost control, compliance, and patient experience.
- Effective engagement requires structure: identifying stakeholders, assessing influence and interest, tailoring communication, and reviewing engagement continuously as conditions change.
Healthcare organisations work with a wide range of stakeholders whose decisions, actions, and expectations directly shape patient care and health outcomes.
In healthcare, stakeholders are individuals or groups that influence, deliver, regulate, or are affected by patient care and health outcomes.
Healthcare stakeholders commonly include patients, clinicians, providers, hospital leadership, regulators, commissioners, suppliers, and community organisations.
Because priorities often differ across clinical quality, cost control, compliance, and patient experience, healthcare organisations need a structured approach to stakeholder engagement (and, ideally, a proper stakeholder management system) to support positive outcomes and reduce risk.
Let's go over the best approach to identify and effectively engage with stakeholders in healthcare.
Who are the stakeholders in healthcare
Healthcare stakeholders generally fall into four core groups: patients, providers, policymakers, and payors, supported by a wider ecosystem of organisations and partners.
In order to identify all your stakeholders (and avoid missing key stakeholders), start by looking into all your information sources - internal systems, spreadsheets, notes - as well as talking to your colleagues and team members.
Collate a list of all the potential stakeholders of your project, research, programme or organisation. Leave no one out at this point.
Internal and external stakeholders in the healthcare sector will include many different groups. Depending on the scope of the project, programme, or organisation, healthcare stakeholders may include:
- Clinicians;
- Patients and family members;
- Healthcare providers;
- Hospitals and healthcare facilities;
- Government agencies;
- Pharmaceutical firms;
- Insurance companies;
- Healthcare (medical) associations;
- Medical tech organisations;
- Staff;
- Investors;
- Local community;
- Public health organisations;
- Non-Governmental Organisations (NGOs);
- Media;
- Research institutions;
- Charities.
From public health and social care to health promotion and research, in general, all healthcare organisations will have the "4 P's" as their stakeholders: patients, providers, policymakers and payors.
Patients
Patients care most about access to care, safety, outcomes, and being treated with trust and respect. Tension often arises when changes to services, waiting times, or treatment decisions are not clearly explained or do not match patient expectations.
Providers
Providers focus on delivering safe, high-quality care while managing workload, resources, and regulatory requirements. Tension typically emerges when operational pressures or system constraints conflict with clinical judgement.
Payors
Payors are responsible for funding care and managing cost, value, and appropriate use of services. Tension can arise when clinical decisions increase costs without clear evidence of improved outcomes.
Policymakers
Policymakers set standards and oversee equity, accountability, and population-level outcomes. Tension often appears when policy requirements affect how services are delivered at a local or organisational level.
It's important to take the time to be thorough and leverage all your data resources. Consider using social media channels to identify stakeholders; it can be a helpful search tool.
Before getting started with the stakeholder communication plan creation, you must determine the needs and requirements of your stakeholders. They will expect different types of information, communication methods and attention.
Once stakeholders have been identified, the next step is stakeholder analysis, which focuses on understanding influence, interest, and decision-making authority.
The healthcare stakeholder engagement lifecycle
1. Identify stakeholders by reviewing internal information and speaking with teams to ensure no key groups are missed.
2. Analyse stakeholders to understand influence, interest, expectations, and decision-making authority.
3. Map engagement approaches by aligning communication methods and frequency to each stakeholder group.
4. Engage and review continuously, using feedback and changing conditions to refine engagement over time.
Healthcare stakeholder analysis
Stakeholder analysis in healthcare is the process of assessing stakeholder influence, interest, and expectations in order to prioritise engagement and tailor communication.
The stakeholder analysis process will provide you with a clear view of the various stakeholders your project impacts and will help you create tailored communication for each stakeholder audience.
To identify the key stakeholders in your project, start with these questions:
- Which stakeholders have a fundamental impact on our project?
- What's the relevance of your relationship with them?
- Who will be responsible or have decision authority on the project?
- What do you want/expect from them?
These will help you classify your stakeholders based on their relative influence and interest in the project.
Then use an interest/influence matrix or the salience model to categorise your stakeholders:
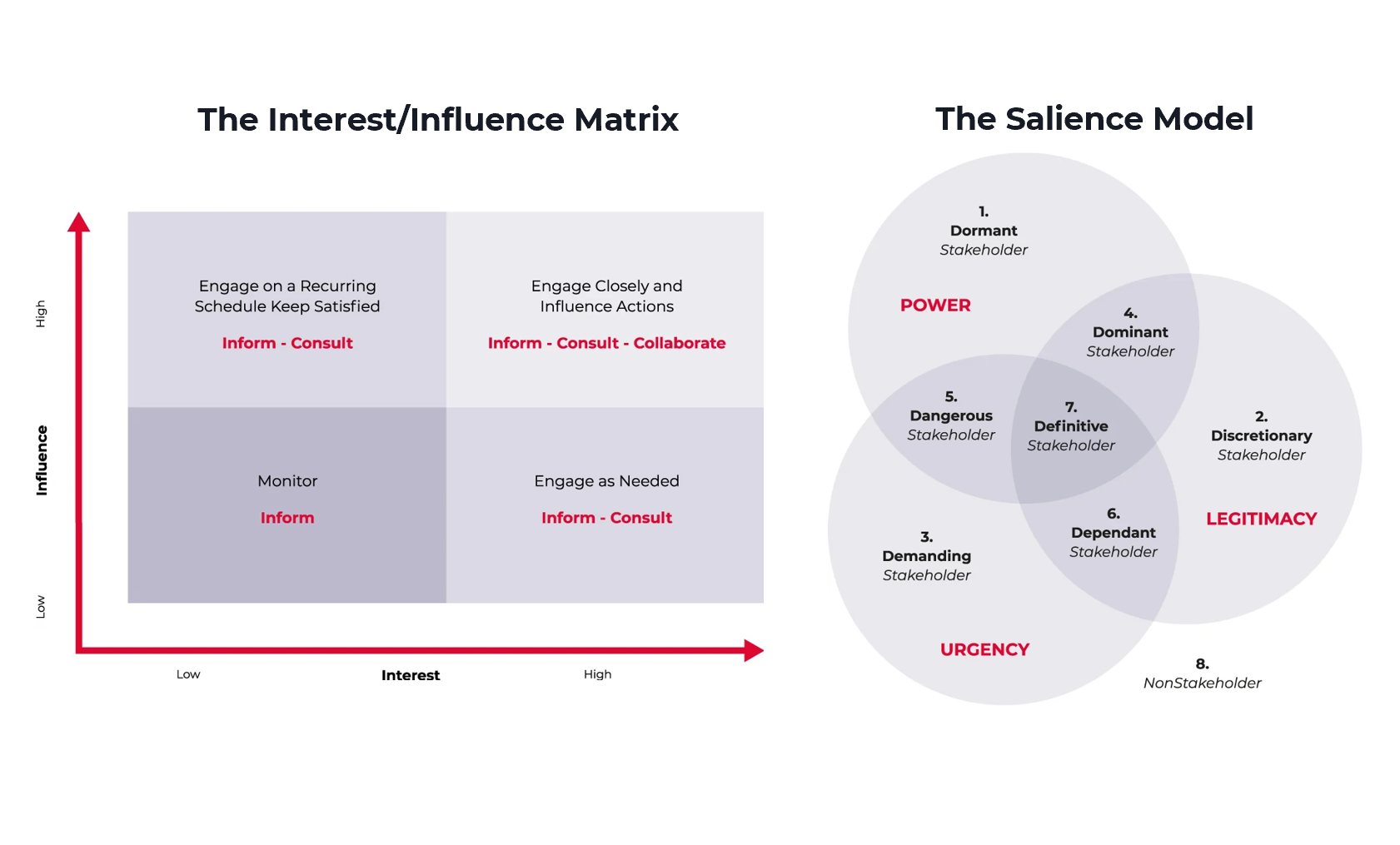
Both methods are part of the stakeholder mapping process that will enable you to determine the appropriate communication type for each stakeholder group.
If planning a public consultation, combining this stakeholder analysis with the RACI model will provide the best support for your consultation.
In case you would like to learn more about how to get started with stakeholder mapping (or review it), check our complete stakeholder mapping guide.
Why effective communication is important
The healthcare industry is highly impacted by its stakeholders, and the interrelationship among them can be quite complex. They can provide research and funding as well as influence strategic direction and public opinion.
That's why stakeholder engagement in healthcare is crucial. By effectively engaging with your different audiences, you will be able to:
- support projects;
- promote patient involvement;
- shape work programmes and the delivery of services;
- learn the issues that matter to your stakeholders;
- support key audiences in understanding your work;
- understand potential risks;
- gather insights and perspectives;
- build positive relationships;
- determine services priorities.
Effective communication and engagement will help you support the different stakeholder groups:
- Patients: help them comprehend the role of your organisation and the challenges you face, so they embrace different care models;
- Partners: enhance collaboration with your community partners, amplifying your voice within the broader health and social care ecosystem;
- Staff: help them feel integrated, ensuring understanding of roles and alignment toward shared goals.
Engaging with stakeholders in healthcare
Stakeholder engagement in healthcare is an ongoing process that builds on stakeholder identification and analysis and must be reviewed as services, policies, and stakeholder needs change.
With your stakeholder groups mapped by interest and influence, you will be able to plan specific strategies to engage with them.
Create a stakeholder engagement plan and map out your communication activities, frequency and tools based on the engagement needs of each stakeholder group.
Stakeholder engagement is a continuous process, where you must monitor engagement activity and use the valuable feedback and insights to shape your services and support your projects.
Regardless of your programme or project size, from building a new hospital to surveying a small group of people, creating a stakeholder strategy and planning the engagement with your stakeholders will allow you to work on the issues that matter to the success of your project and your stakeholders.
Proactive communication strategies
There are numerous engagement activities you can implement to maximise your stakeholder engagement - workshops, events, forums, focus groups, surveys, text messages, and newsletters. Here are a few strategies you can adopt:
-
Assess the tools you have at your disposal: use the available tools, such as websites, social media, and newsletters, to disseminate information according to what your stakeholder groups need to know.
- Community engagement: collaborate with community partners, such as local councils, churches, schools and community groups to leverage their communication channels.
-
Utilise media (social and others): understand what local media and social media platforms your stakeholders follow and use, and be present there as well.
-
Establish communication schedule: implement a schedule for communication activities, balancing updates on developments with relevant health and self-care information.
-
Patient participation groups: work with patients to test communication materials, to ensure relevance and effectiveness.
- Collaborative approach: share communication expertise across the organisation to streamline efforts, minimise duplication, and distribute workload effectively.
-
Set expectations: prioritise practical and sustainable communication strategies to avoid over-commitment and ensure long-term engagement.
The importance of stakeholder data security in healthcare
When it comes to stakeholder information, the healthcare sector is a valuable target for malicious cyber activity as it handles highly sensitive personal data and intellectual property for research.
Human error and process errors can also harm sensitive data, resulting in data breaches and data loss.
Having personal details wrongly shared with strangers not only causes fear and leads to thousands (or even millions) in costs and compensation, but it can also damage an organisation's reputation and confidence.
Using multiple platforms or spreadsheets to manage your stakeholder engagement can increase the risk of data errors and the time wasted on repetitive tasks (as well as having to manage login in and out of several systems).
Selecting a stakeholder engagement solution that meets data privacy requirements and has a high level of data security can prevent serious risks and reassure your stakeholders that their information is being handled with the utmost care.
What effective stakeholder engagement in healthcare requires
Successful stakeholder engagement in healthcare is an ongoing and structured practice that supports the delivery of sustainable care.
Healthcare organisations that master this practice do three things well: they clearly identify who their stakeholders are, understand how influence and interest differ across groups, and engage each audience using the appropriate communication method.
Organisations that adopt stakeholder engagement as a vital part of their business are better at adapting to the ever-changing needs of stakeholders, strengthening trust, reducing risk and delivering better outcomes for their patients and communities.
Stakeholder engagement is not optional. It is essential infrastructure for delivering care that works.
Deliver a consistent approach to stakeholder engagement in healthcare
Being able to engage with your stakeholders in the right way at the right time is invaluable to supporting the outcomes of any healthcare organisation.
Tractivity is helping many Healthcare organisations, including the NHS, to support consistent patient involvement and build positive relationships through a complete set of communication tools for patient engagement.
Download the Supporting the NHS whitepaper and discover why many NHS organisations are choosing Tractivity, and contact us to learn more about how we can help you.


